As businesses of all sizes have entered the age of digital transformation, the recent increase in cyberattacks is dramatic. In 2022 alone, there’ve been 433 million ransomware attacks on organizations. The numbers will only worsen with the prevailing use of the cloud for operations and the adoption of more advanced technologies.
This article examines what network vulnerability assessment entails and its critical role in security risk mitigation for your business.
What is network vulnerability assessment?
Network vulnerability assessment is a process to find and analyze weaknesses or gaps in network infrastructure that hackers could exploit. Organizations enlist the help of cybersecurity service providers to identify potential vulnerabilities and prioritize their remediation. The assessment can be done manually or with automated vulnerability scanning tools.
Part of post-assessment vulnerability management, network vulnerability testing helps businesses prevent or reduce the impact of cyberattacks, comply with regulatory requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, PCI SSC, etc.), and improve the security posture.
ASSESS YOUR NETWORK VULNERABILITIES WITH EPAM STARTUPS & SMBS
Our cybersecurity team will help you detect and mediate your security issues before it’s too late.
Types of vulnerabilities to watch out for
Hackers could exploit several types of network vulnerabilities to breach a network. In doing a network security assessment, we put them into the following broad categories:

Hardware endpoints
All the devices in a network can be a point of failure unless the IT department is aware of them and maintains each one with firmware upgrades for known flaws. Some of the most common hardware issues include:
- Physical network devices: One of the quickest and easiest ways to infiltrate a network is by plugging in a device loaded with a virus or malware. The malware can quickly be injected using USB drives to install spyware or a backdoor code that captures sensitive data.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi is a convenience all businesses use, but one that opens them up to attacks, as it gives users access beyond firewalls. Without password protection, intruders could find a way into the network and wreak havoc.
- IoT devices: Interconnected devices, including lights, thermostats, and locks, are all the rage. They have sensors and software that allow them to connect to systems, networks, or devices and transmit data over the internet. They may be convenient, but they are not always well-secured and are almost impossible to update. An internet vulnerability assessment can show you potential points of exposure. The best safeguard is not to use them at all. Still, where convenience is required, it is recommended that you source them from reputable sellers and connect them to a separate subnet to reduce contact with the primary network.
- Unauthorized devices: USB drives are notorious for their convenience when spreading malicious apps or stealing data because they are small, portable, and can store different file types. Other devices to watch out for include digital cameras, printers, MP3 players, etc. With network vulnerability monitoring policies, such additions to the network can be located and remediated before they do any harm.
Software
No matter how sophisticated a network is, it uses different types of software, including operating systems and apps, to run business processes. If any software used has a flaw, it is only a matter of time before a hacker finds and uses it.
Some of the network security threats associated with software security vulnerability include:
- Outdated or buggy software: Unpatched software continues to be one of the most significant sources of network vulnerabilities and could expose your business to avoidable attacks. The security team should ensure that the software is updated to keep up with security patches for known issues.
- Shadow IT (unauthorized software): Sometimes, employees download software and bring it to the workplace without getting IT approval. Since not many people have information security training, these pieces of software could increase the attack surface area and expose you to risks you didn’t even know were in the system. IT teams and employees must have a relationship that allows for precise and open communication regarding unauthorized software.
- Misconfiguration: Configurations done incorrectly or not at all can contribute to security loopholes that may allow unauthorized access. Web applications often come with default settings, including passwords, designed to make setting up and using the tools more accessible. Proper configuration ensures that none of these doors are left open or undefended in case of an attack.
Penetration testing is a great way to find issues cybercriminals might exploit. You can also introduce the secure SDLC (the software development life cycle), where software is developed with all the cybersecurity measures in place, to prevent flaws from entering the code.
People
Even with all our software and physical equipment protections, they require people to manage, and people make mistakes that could be exploited.
Some of the problems found in the network vulnerability assessment process focused on employees and users include:
- Weak passwords: People use passwords they can easily remember or the same password for everything. The result is many weak passwords inside and outside of work, making it easier to hack the organization by exploiting weaknesses introduced by people. An organization can implement password generators to create unique passwords that aren’t easy to hack or guess. Multi-factor authentication can also help significantly reduce the threat of password theft and subsequent data breaches.
- Social engineering: Social engineering is a fancy term used by security experts to describe tactics that rely on the fact that you can trick people. Scam calls, phishing emails, and fake websites are all used to gain access to sensitive information within systems. The best way to guard against this is awareness. An organization should ensure that employees know what to watch out for and that policies are implemented to prevent damage.
The IT team can also ensure that all employees have as much access as they require and do not have access to anything they do not need, just to be safe.
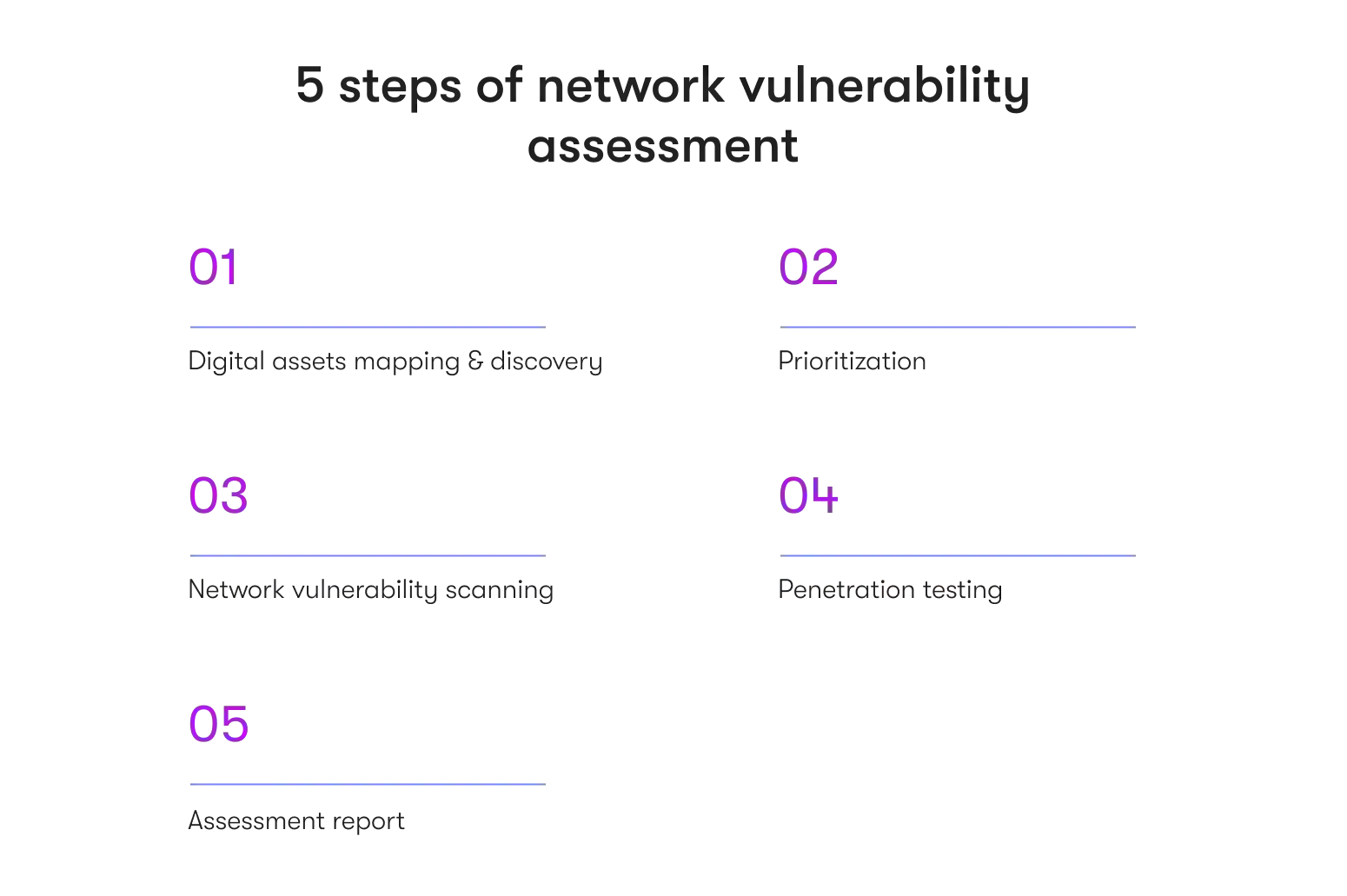
Network security vulnerability assessment in 5 steps
So, what are the steps involved in a network cybersecurity audit?
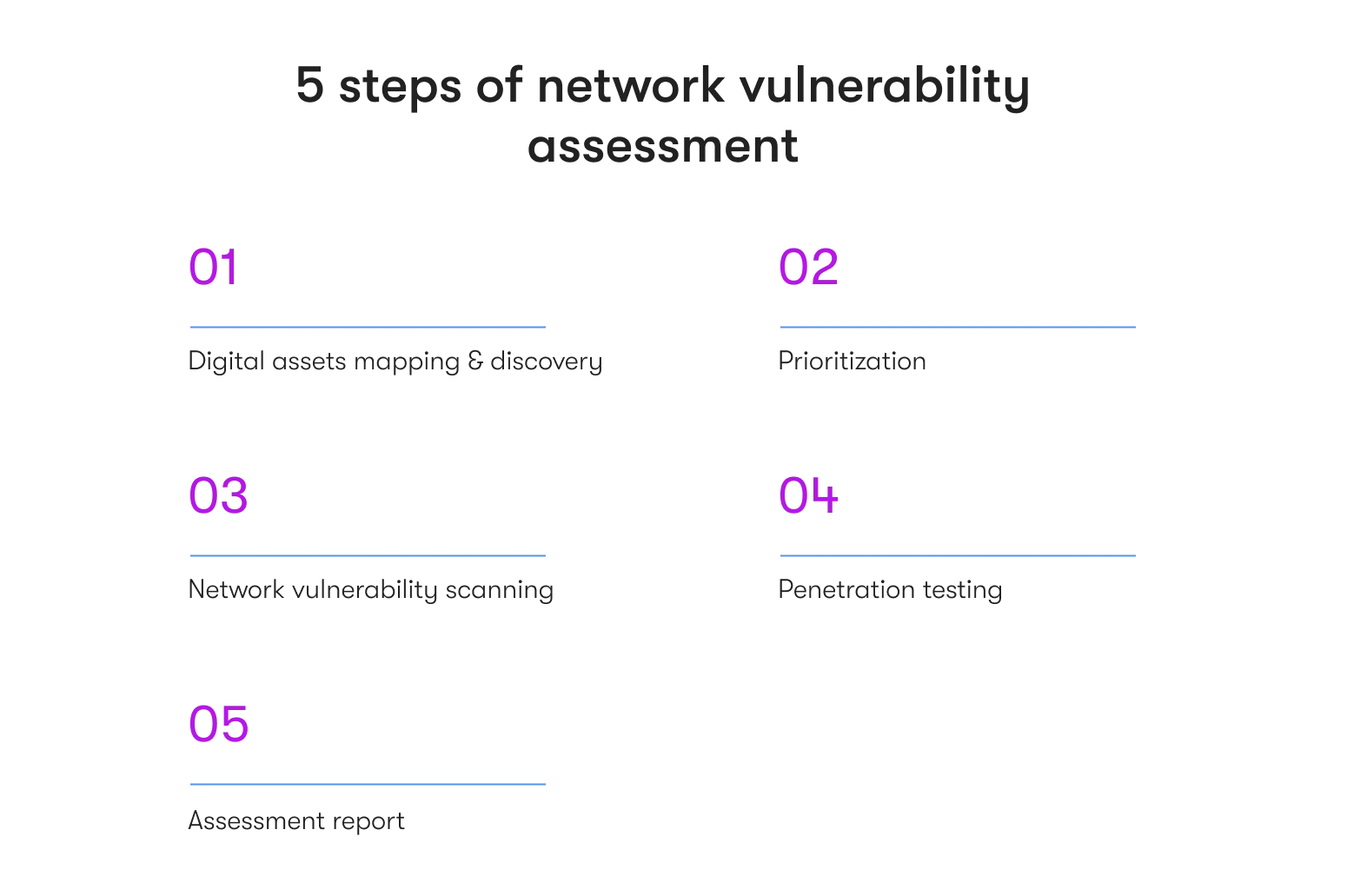
1. Digital assets mapping & discovery
Behind the scenes, in the bowels of the IT dungeon, a mess of servers, IoT devices, mobile devices, routers, etc., work tirelessly to keep business processes going.
Network security vulnerability assessment starts with the discovery of these assets to know what is connected to the network. With the right vulnerability assessment tools, you can discover public-facing systems as well as connect to cloud providers to bolster cloud network security.
2. Prioritization
After you find out what you have, the next question is whether you can afford to run a vulnerability assessment test that covers everything. The preferable way to do this is to run a vulnerability assessment on the entire network, but often it doesn’t work out like that.
Some vendors tend to charge per asset, which means you have to prioritize what is most at risk, as you may not be able to or might not need to cover every asset your company owns.
Consider the following parameters when choosing what to prioritize:
- Severity
- Exploitability
- Projected impact
- Threat intelligence
- Business needs/context
You can start with internet-facing systems and servers, customer-facing apps, employee devices, and databases containing necessary information.
Alternatively, you can opt for managed cybersecurity services to ensure your network is monitored and protected at all times.
3. Network vulnerability scanning
Vulnerability scanners are designed to find known security weaknesses and offer insights into how they can be patched. Because the vulnerabilities are usually publicly reported, we know a lot about them.
Scanners use publicly available information to identify vulnerable devices and software in an organization. The scanners will send probes to find running services, open ports, configuration settings, software versions, and more.
The information is used to identify many known vulnerabilities in the system being tested. In addition, there are more probes sent to find individual vulnerabilities, which can only be used by sending a safe exploit to prove the weakness exists.
These kinds of probes may surface common vulnerabilities that include cross-site scripting, or command injection, or passwords and usernames that were never changed from the default.
4. Penetration testing (pentesting)
A type of security testing, pentesting uses a combination of automation and hands-on techniques to simulate ‘hacking’ a network before real hackers do. Usually hired specifically for the purpose, pentesters are sometimes known as white hat hackers, given that their goal is to help you better secure your network with offensive security techniques.
The offensive security focus includes web and mobile apps, APIs, digital ecosystems, infrastructures of all types, as well as people (users and employees).
5. Network vulnerability assessment report
When the vulnerability assessment is finished, the security team will carry out the vulnerability analysis and give back an assessment report to let the organization know what has been found. The report will list all the identified vulnerabilities, index them by severity, and recommend fixes.
A comprehensive network vulnerability assessment report typically includes the following:
- Executive summary: This section contains an overview of the purpose, scope, methodology, and assessment results, emphasizing the main findings and recommendations for fixes.
- Scan results: This section explains the scan results, including how the vulnerabilities are categorized and ordered, what types of reports are included, and what tools and tests were used for the scan.
- Findings: This is where the list of vulnerabilities is expounded on, along with severity, description, fix, and count information. It also shows which systems were scanned and which were not, along with the reasoning behind the choices.
- Recommendations: This section gives a complete list of actions that you should take to fix the flaws, as well as other security policies, tools, and configurations required to enhance network security.
With the report, your IT team can quickly identify and patch each problem with the appropriate fix and be aware of what is included in the network for future safeguarding.
GET FULL-CYCLE NETWORK VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT AND FIXES BY OUR EXPERT TEAM
With 400+ security engineers and consultants, we help businesses to efficiently secure their network perimeter.
Network vulnerability assessment checklist
To help you understand if your current security measures are adequate or whether you need to upgrade protections, we have prepared a network vulnerability assessment checklist:
- What are the main business objectives of your organization?
- What are your most valuable and sensitive assets or data to protect?
- What are the current security policies and procedures followed by your organization?
- How often do you perform vulnerability assessments and audits on your network infrastructure?
- What are the main risks and threats your organization faces?
- How do you monitor and respond to security breaches and incidents?
- How do you measure and report on the effectiveness and performance of your security protection?
- Do you conduct employee and customer security awareness campaigns?
- How do you ensure compliance with relevant industry laws, regulations, and standards?
- What are the current gaps in your organization’s network security?
- What are the expected outcomes or benefits of upgrading your network cybersecurity protections?
Assess your network vulnerabilities with EPAM Startups & SMBs
If you’re a startup or a small business, you know how important it is to protect your network from cyberattacks. Any negative impact on your reputation, revenue, and operations could be damaging in a way that’s hard to come back from.
Enter EPAM Startups & SMBs that provides managed cybersecurity solutions for startups and small businesses. EPAM Startups & SMBs can help you assess your network vulnerabilities, implement best practices, and monitor and respond to security incidents.
We can also help with compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001. Our experienced cybersecurity experts use the latest tools, technologies, and best practices to scan your network, detect vulnerabilities, and prevent exploitation.
FAQ

Expert digital communicator and editor providing insights and research-based guides for technology buyers globally.
Expert digital communicator and editor providing insights and research-based guides for technology buyers globally.
Explore our Editorial Policy to learn more about our standards for content creation.
read more